SAGE designed and engineered a bespoke control system that autonomously manages energy generation, conversion, and allocation for solar and grid-derived energy, balancing this against operational electricity requirements in real-time.
Phase 2 of ZCEF involved the connection and interfacing of 46 SMA Solar Central Inverters (across 14 sites), 61 Wall Mount Inverters (across six sites) and nine Tesla Powerpack battery systems to develop an overarching Power Management System.
The Power Management System interfaced between SA Power Networks and AEMO grid connection data, SA Water’s SCADA systems and various existing plant metering in order to command the battery and solar controller, balancing the power between the solar and batteries generation.
The system also monitored and controlled ancillary equipment such as solar panel sun tracking systems and weather monitoring stations.
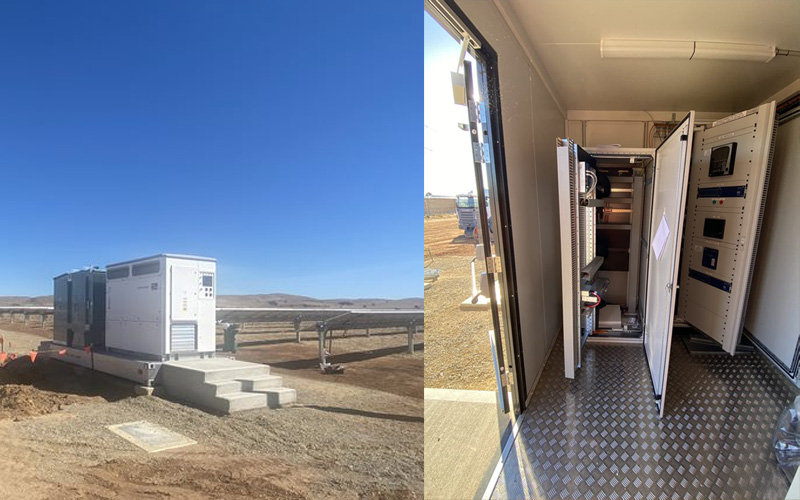 An SMA Australia Central Inverter (pictured left) and control room (right) at SA Water's Mannum Plant, form part of the connected Power Management System.
An SMA Australia Central Inverter (pictured left) and control room (right) at SA Water's Mannum Plant, form part of the connected Power Management System.
The Power Management System included alarms and shutdown mechanisms to compare output with grid requirements to ensure SA Water remain compliant with ElectraNet, SA Power Networks and AEMO regulations.
The system also interfaced with the power protection systems to notify SA Water when a site fault occurs or the system is unable to meet the AEMO bidding targets, providing valuable data enabling real-time decision-making for cost saving, maintenance, and easier reporting for compliance obligations.
The system integrates communication to AEMO for NEM bidding data and SA Power Networks or ElectraNet grid setpoints, calculating the solar and battery generation allowed to maximise energy production.
The NEM has an energy bidding system every 5 minutes and 30 minutes, with pricing changing based on market demand and available energy on the grid. The Power Management System enables SA Water to adjust energy generation at each separate site in real-time, maximising energy production for the NEM while retaining optimal energy requirements for SA Water to remain efficient at all times.
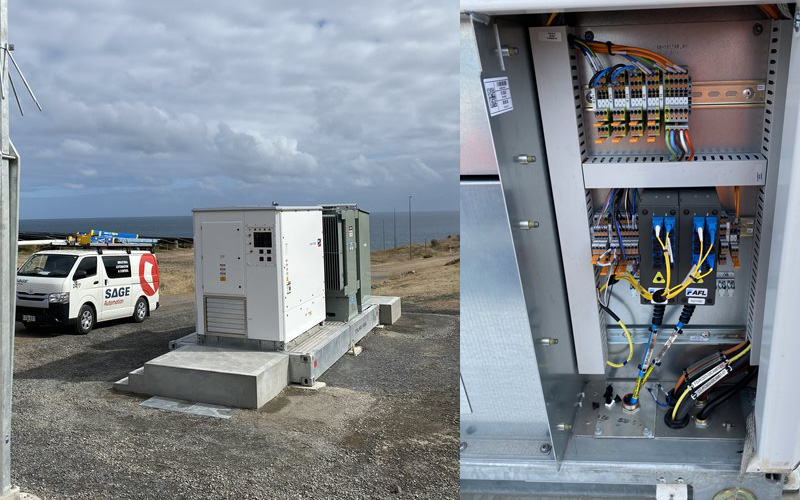 An SMA Central Inverter (pictured left), and some termination in its interior (right) at SA Water's Adelaide Desalination Plant.
An SMA Central Inverter (pictured left), and some termination in its interior (right) at SA Water's Adelaide Desalination Plant.
For SA Water's Happy Valley, Mannum 2 and Mannum 3 sites, SAGE, in partnership with subcontractor Specialised Solutions, provided new solar/battery control rooms for the project.
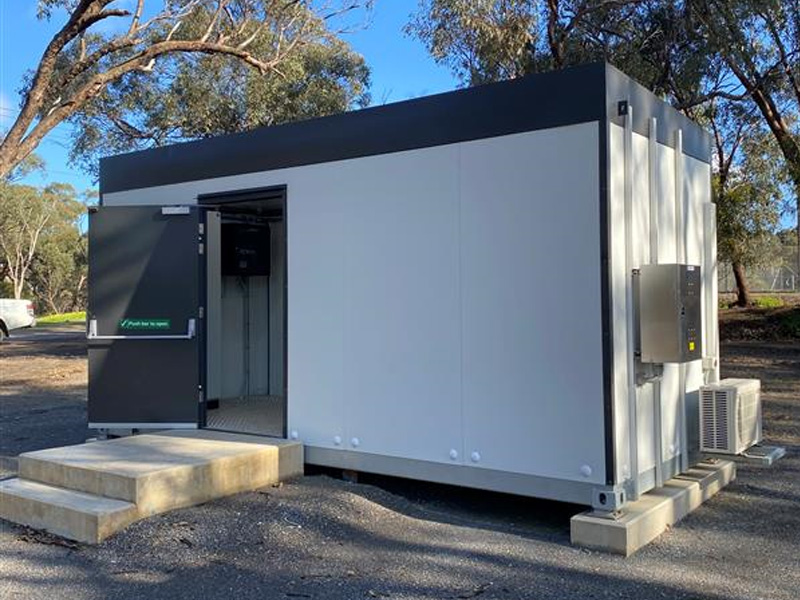 A purpose-built solar/battery control room at Happy Valley.
A purpose-built solar/battery control room at Happy Valley.
The Power Management System had to interface to a wide variety of energy generation systems, multiple electricity providers and AEMO, various ancillary equipment and existing site control systems for some sites. A system capable of communicating to a variety of systems while maintaining high performance in order to control the energy generation in real-time was required. Schneider Electric’s Modicon M580 Ethernet Programmable Automatic Controllers (ePACs) were a perfect fit for the project requirements, supporting the delivery of a highly modifiable, scalable, and future-proof solution.
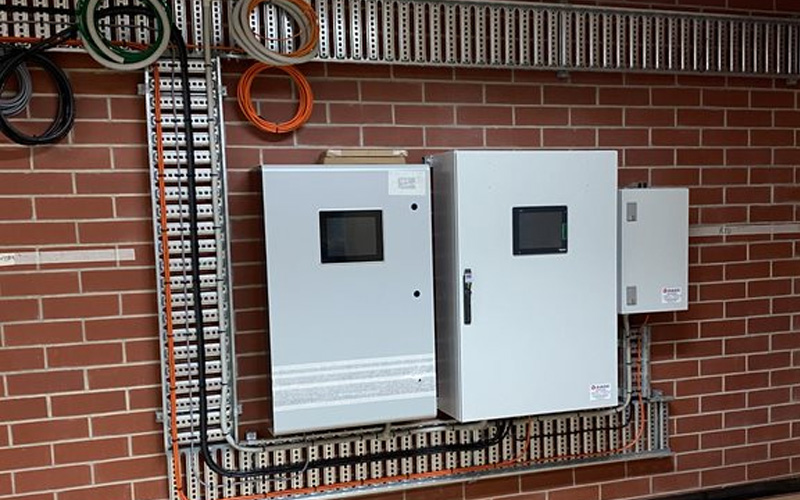 Newly installed control panels in SA Water's Murray Bridge control room.
Newly installed control panels in SA Water's Murray Bridge control room.
The software for the Schneider M580 ePACs was developed using a modular coding standard, allowing for different calculation elements, hardware interfaces, and alarming groups to be created for each site’s unique hardware elements, grid connection requirements and existing plant systems. The system also has future capacity to allow for future additions and enhancements.
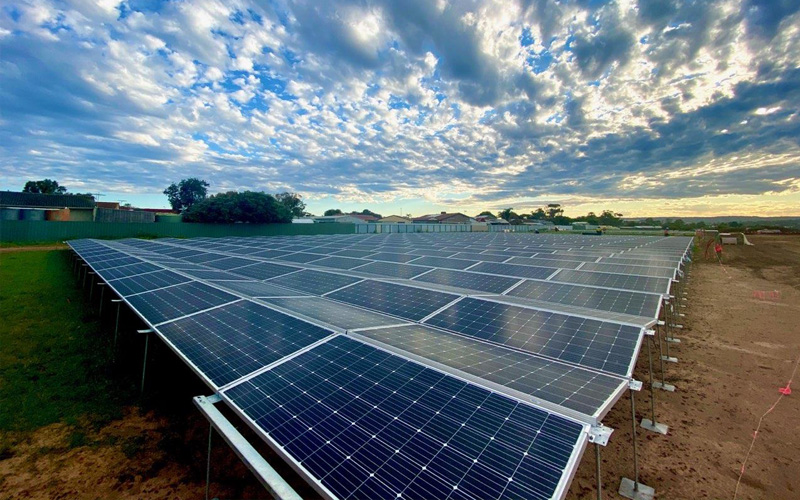
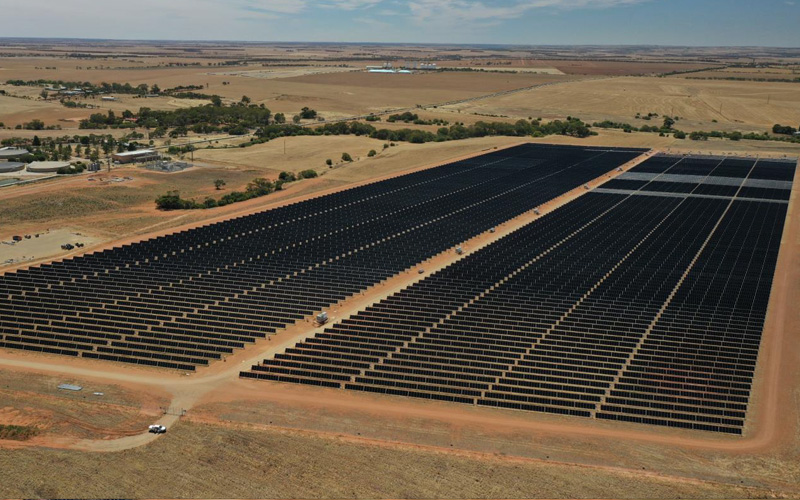

 New solar panels at SA Water's Mannum Plant. Image courtesy of Enerven.
New solar panels at SA Water's Mannum Plant. Image courtesy of Enerven. An
An  An SMA Central Inverter (pictured left), and some termination in its interior (right) at SA Water's Adelaide Desalination Plant.
An SMA Central Inverter (pictured left), and some termination in its interior (right) at SA Water's Adelaide Desalination Plant. A purpose-built solar/battery control room at Happy Valley.
A purpose-built solar/battery control room at Happy Valley. Newly installed control panels in SA Water's Murray Bridge control room.
Newly installed control panels in SA Water's Murray Bridge control room.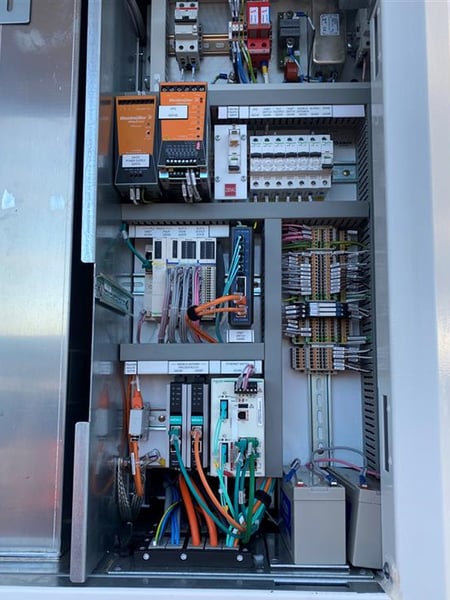 One of the SMA Solar Central Inverters, featuring new equipment installed by SAGE.
One of the SMA Solar Central Inverters, featuring new equipment installed by SAGE. 




